Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (Sverige)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
11.1 Plan Risk Management
"The process of defining how to conduct risk management activities for a project."
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
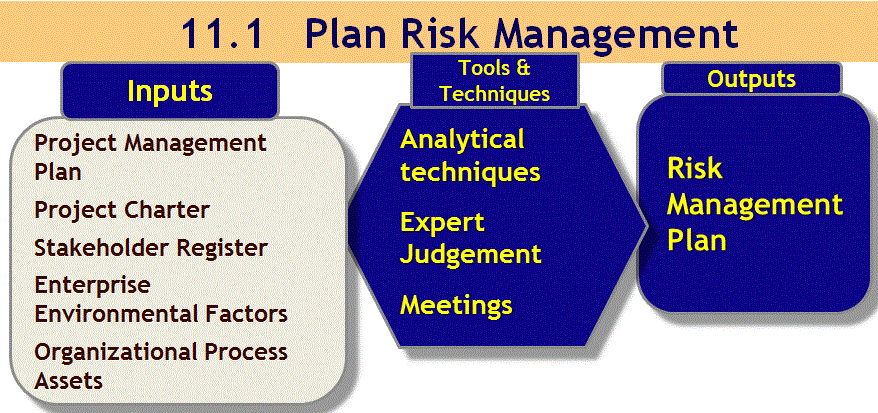
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 11-2 Page 313
Risk Definitions
- Risk Appetite – the degree of uncertainty an entity is willing to take on in anticipation of a reward
- Risk Tolerance – the degree, amount, or volume of risk that an organization or individual will withstand
- Is there an organizational Risk Policy?
- Risk Threshold – above (risk will not be tolerated); below (risk will be accepted)
- Different stakeholders will have different risk tolerance
- Known risks (known unknowns) can be identified and managed
- Unknown risks (unknown unknowns) are not identified and therefore cannot be managed
What is Risk?
An uncertain event or condition, which if it happens, will have an effect on one or more project objective
May have a positive or negative impact. Need to consider:
- The probability that the risk event will occur.
- The impact of the risk on a project should it happen.
Three elements when stating a risk:
- Risk cause: There is a risk that the food may not have been cooked sufficiently
- Risk event: When we go to the team building event and have a Chinese dinner in the restaurant
- Risk effect: Which could lead to food poisoning for one or more of us resulting in not being able to take the PMP exam
Risk Management – Project Life-Cycle
The objective of Project Risk Management is to decrease the likelihood and impact of negative events, while increasing the likelihood and impact of positive ones
All projects contain risk!
- “Zero risk” is not an option
Risk versus Return
- Higher potential risk = higher potential return
- No risk = no return
Many companies have a combined Risks and Issues Log
PM and project team always looking for :
- New risks
- Early warning signs or triggers for existing risks
- Changes in severity of existing risks
Risks & Issues
Issue
- A negative project risk that has occurred
- Carry out identified actions
- If it could happen again – raise as a risk
Requires reactive actions now or later
Risk
- Could happen in the future
- Uncertain – need to evaluate impact and probability
- We have time to plan – may or may not need to action
- Possibly risen from an existing issue
Requires proactive actions
Inputs
Project Management Plan
- Cost Management Plan
- Project budget – contingency reserve and management reserve
- How reserves will be estimated, managed and reported
- Schedule Management Plan
- How the schedule contingencies will be handled
- Communications Management Plan
- Reporting on risks, their responses and potential impacts
Project Charter – high level risks
Enterprise Environmental Factors
- Organizational attitudes and tolerances to risk
OPAs to be Consulted
- Risk Categories, stakeholder register, templates, delegated authority levels (risk decisions), historical information
Tools and Techniques
Analytical Techniques
- Stakeholder Risk Profile Analysis
- Strategic Risk Scoring sheets
Planning Meetings can discuss
- Risk identification, assessment, quantification by team members
- Schedule of activities
- Approach to contingency and management reserves
- What templates will be used or constructed
- Meaning of terminology used
- Awareness/use of the Probability/Impact Matrix
Expert Judgement
Risk Management Plan
Typical contents include:
- Methodology - the tools, techniques and approaches to be used to for risk management
- Roles and Responsibilities for each risk management action
- Budget - project risk management activities.
- Time - Defines how often the risk management activities will be performed throughout the project life cycle
- Risk Categories
- Definitions of Probability and Impact – scales used in qualitative risk analysis
- Probability and impact matrix
- Revised stakeholder tolerances – these may need to be updated as a result of the plan risk management process
- Reporting Formats - how outputs of this process will be documented, analyzed, and communicated
- Tracking – how risks activities will be recorded
Source: http://www.infosys.com
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/se/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group