Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (Sverige)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
4.4. Monitor and Control Project Work
- The "process of tracking, reviewing and reporting the progress to meet the performance objectives"
- Requires project baselines; the actions required to ensure project performance matches expectations.
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 4-8 Page 86
- Allows stakeholders to understand:
- Current state
- Impact of changes
- Forecasts for budget, scope and schedule
- Work performed
- Also takes time to monitor risks, implemented changes and forecasting and reporting change
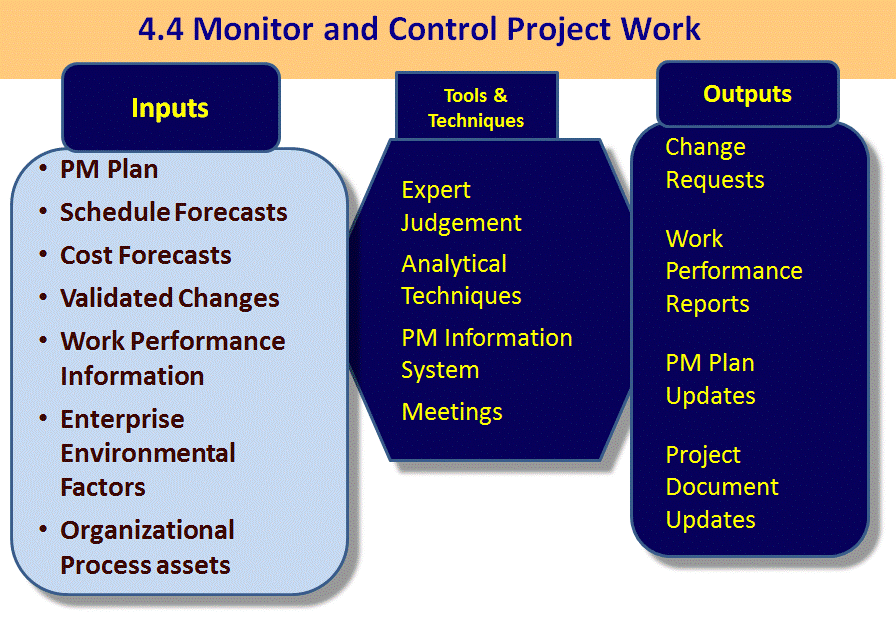
Inputs
- Project Management Plan
- Forecasts for Schedule and Cost
- Validated Changes
- Validation of implemented actions following a change request authorisation
- Confirms that they were implemented appropriately
- Happens in 8.3 Control Quality (page 252)
- Different to verifying the correctness of deliverables
- Work Performance Information
- Enterprise Environmental Factors
- Organizational Process assets
Question - Exercise
What are the aspects of project management, that you as a Project Manager, will monitor during their performance in the project?
Brainstorm a series of ideas - Answer is below.
Exercise Answer
- Performance Information
- Actual costs and value of work performed, comparing it to forecast and actual costs
- Implementation of validated changes and monitoring them
- Defect repairs, impact on budget and schedule
- New risks (analysis, responses); tracking monitoring existing; reporting status; implementing response plans; workarounds
- Keeping and maintaining work performance data / information
- Getting this together to enable 10.2 Manage Communications
- Collecting, measuring and distributing performance information
- Assessing measurements and trends
- Identifying bottlenecks or areas of concern
- Control -> corrective/preventive actions; replanning; follow up on actions already planned
Tools and Techniques
Looked at here:
- Regression Analysis
- Grouping Methods
- Causal Analysis
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA)
Looked at later:
- Fault Tree Analysis
- Root Cause Analysis Forecasting Methods Reserve Analysis Trend Analysis
- Earned Value Management
- Variance Analysis
Regression Analysis - "An analytic technique where a series of input variables are examined in relation to their corresponding output results in order to develop a mathematical or statistical relationship"
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
Grouping Methods - Grouping data (multi parameter datasets) using computer based modelling techniques
Causal Analysis - a method of problem solving that tries to identify the root causes of faults or problems which cause operating events
Fault Tree Analysis - a top down, Deductive reasoning failure analysis in which an undesired state of a system is analysed using boolean logic to combine a series of lower- level events.
e.g. used to determine the probability of a safety accident or a particular system level (functional) failure.
Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) - Developed by reliability engineers in the 1950s to study problems that might arise from malfunctions of military systems. It Involves reviewing as many components, assemblies, and subsystems as possible to identify failure modes, and their causes and effects. A FMEA is used to structure Mitigation for Risk reduction based on either failure (mode) effect severity reduction or based on lowering the probability of failure or both
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/se/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group