Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (Danmark)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
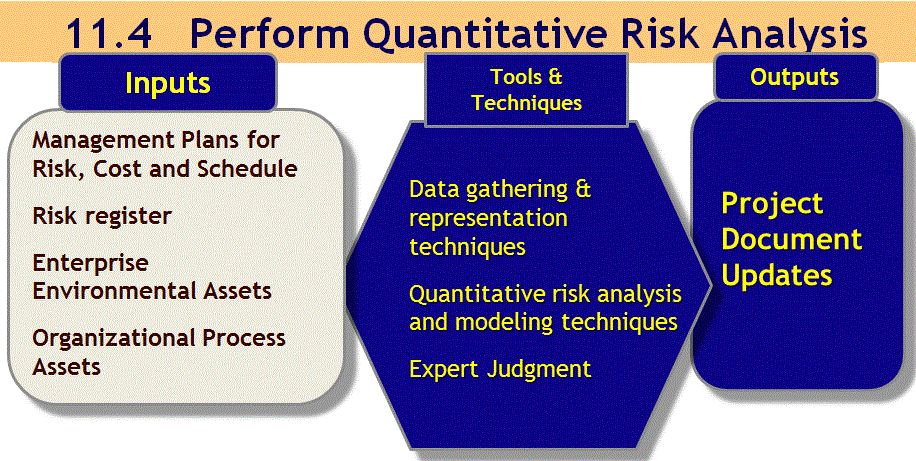
11.4 Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
"The process of numerically analysing the effect of identified risks on overall project objectives."
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 11-11 Page 334
Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
Numerically analyzing the effect of risks on project objectives:
- Perform quantitative analysis normally follows perform qualitative analysis
- When the risks are ranked high enough to make this worthwhile
Sensitivity Analysis
- Identifying those risks that the project objectives could be most impacted by
- Results presented as a Tornado diagram
- One diagram per objective
- Worst case to best case
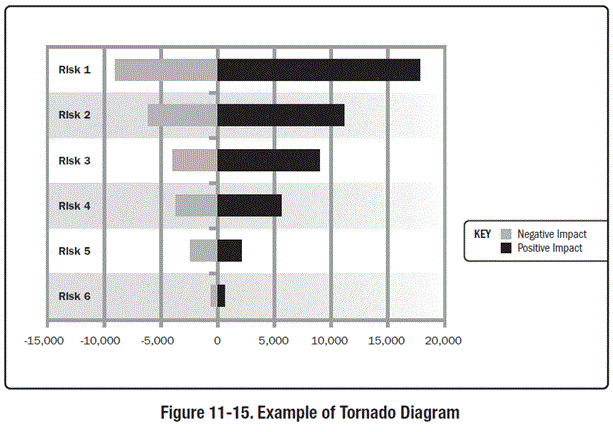
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 11-15 Page 338
Data Gathering & Presentation
Interviewing
- Team members and risk experts
- To quantify the P and I of the highest ranked risks
- Collecting values for 3 point estimating
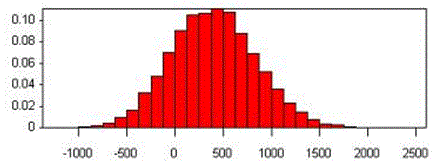
Probability Distributions
- Provides a means of representing risk data and modelling a range of potential outcomes
Expert Judgement
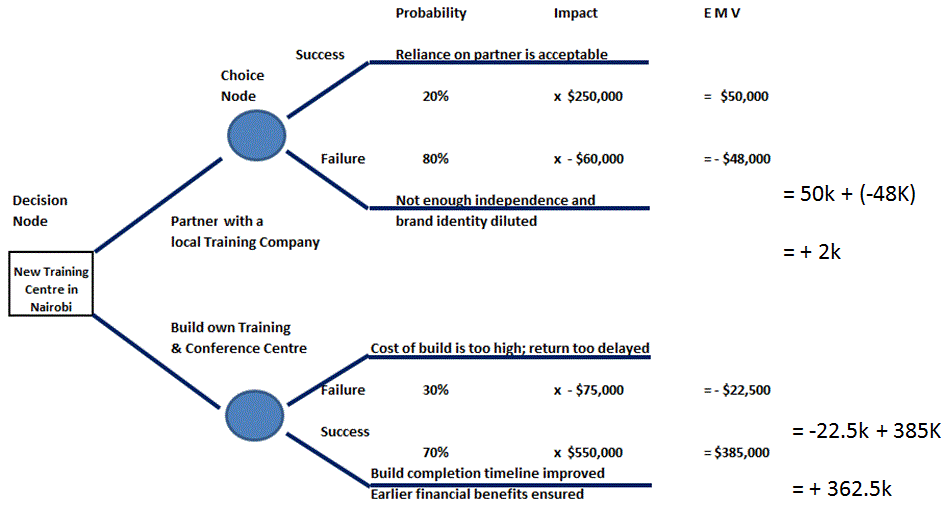
Decision Tree Analysis
- Build own Centre has an Expected Monetary Value of $362,500 (= $385,000 – $22,500)
- Partnering Option has an E.M.V. of $2,000 (= – $48,000 + $50,000)
- Based on this, the Build Own Centre option is selected over the other as it has a larger E.M.V.
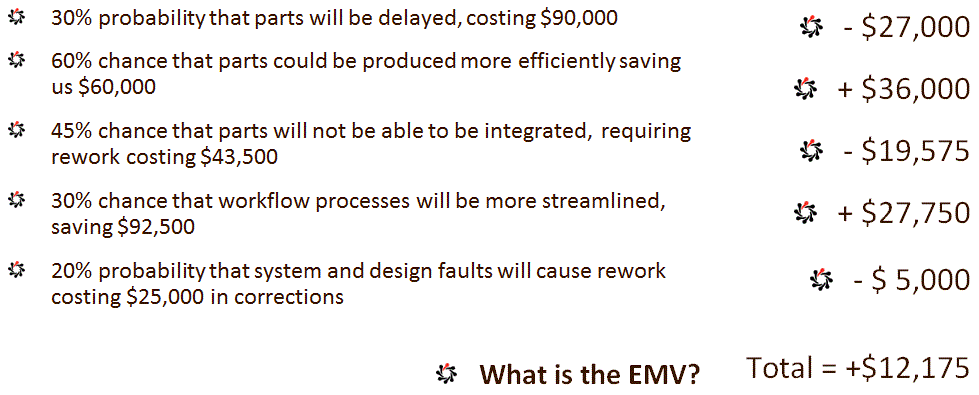
Exercise
You are planning modifications to a car assembly line. We have identified particular project risks and assessed them as shown below. There is a:
- 30% probability that parts will be delayed, costing $90,000
- 60% chance that parts could be produced more efficiently saving us $60,000
- 45% chance that parts will not be able to be integrated, requiring rework costing $43,500
- 30% chance that workflow processes will be more streamlined, saving $92,500
- 20% probability that system and design faults will cause rework costing $25,000 in corrections
What is the EMV?
The Monte Carlo Technique
Uses
- Will select input values – pessimistic to most likely to optimistic and all numbers in between
- A probability distribution is calculated from the iterations i.e. total cost or completion date based on what was input – cost estimates or schedule network diagram and duration estimates
Calculates
- Number of times each activity is on the critical path
- How sensitive the output is to a change in the activity and its duration
Helps to assess and decide
- On the priority of dealing with the risks depending on the impact on the project
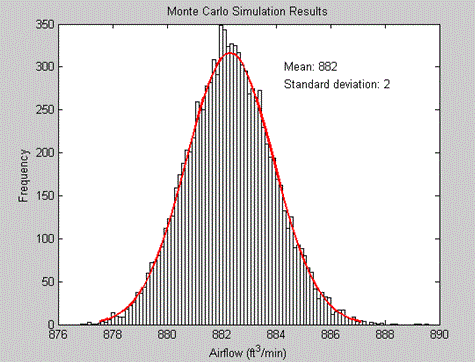
Source http://www.mathworks.co.uk/company/newsletters/articles/improving -an-engine-cooling-fan-using-design-for-six-sigma-techniques.html
Journey Times example
Your Project requires a journey from A to B which has
- 12 traffic junctions in between, with an average time between junctions of 10 minutes
- And a wait time of 3 minutes at each junction when it is on red
Worst case is when all the lights are on red
- = (12 x 3) + (12 x 10) = 156 minutes
Best case is when all the lights are on green
- = 12 x 10 only = 120 minutes
Most probable is when half are on red and half on green
- = (12 x 10) + (6 x 3) = 138 minutes
Need to take other possible combinations into account. This is what Monte Carlo does via software, you will not have to do this technique for the exam, but do need to understand it.
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/dk/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group