Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (United Kingdom)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
11.3 Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
"The process of prioritising risks for further analysis or action by assessing and combining their probability of occurrence and impact."
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
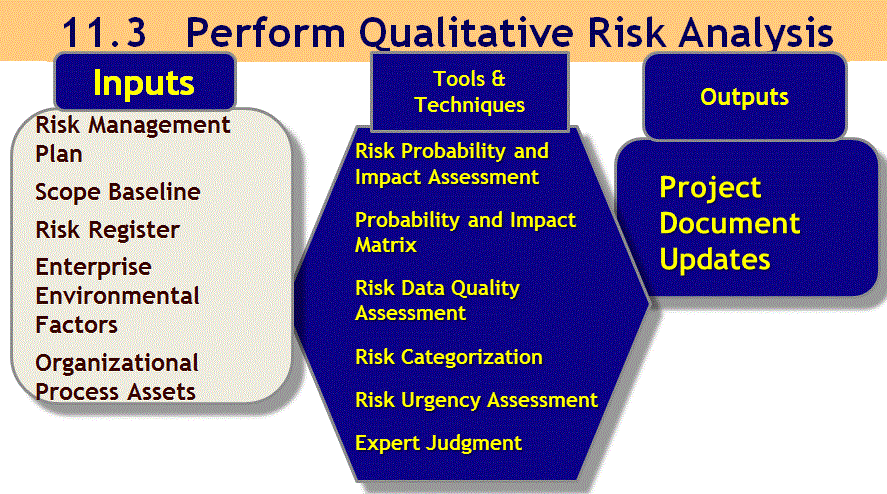
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 11-8 Page 328
Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
- Prioritize risks for further analysis or action
- Assess quality of risk data
- Examine Risk Categories
- Update Risk Register
- Ranking
- To evaluate the overall risk ranking for the project
- To produce a list of prioritised risks
Qualitative tools:
- Probability / impact risk rating matrix
- Intuition / expertise
- Scoring scales e.g.1 to 5; high-medium-low
- Definitions of their meaning
- Risk Urgency – those requiring near term responses
- Can be combined with Ranking to give a final severity rating
Qualitative Risk Analysis Example
|
Probability Analysis |
||
Category |
Qualitative |
Quantitative |
|
A - Very high |
Repeated incidents that could occur several times in the operating life of the facility |
Probability of 1 event in 100 plant years or a frequency equal to 1 x 102 or greater |
|
B - High |
Isolated incidents that could occur limited times in the operating life of the facility |
Probability of 1 event in 1000 plant years or a frequency equal to 1 x 10-2 to 1 x 10-3 |
|
C - Marginal |
An incident occurring sometimes in similar or like facilities elsewhere in the world |
Probability of 1 event in 10,000 plant years or a frequency equal to 1 x 10-3 to 1 x 10-4 |
|
D - Low |
An incident that has occurred more than once in similar or like facilities |
Probability of 1 event in 100,000 plant years or a frequency equal to 1 x 10-4 to 1 x 10-5 |
|
E - Very Low |
Rare incident that has been heard of occurring in similar facilities |
Probability of 1 event in 1,000,000 plant years or a frequency equal to 1 x 10-6 or lesser. |
Risk reduction of hazardous chemical releases
Source: http://www.safetyonline.com/doc.mvc/RISK-BASED-APPROACH-FOR-HAZARD-DETECTION-Fire-0001
Presenting the Results
Method One – Tabular
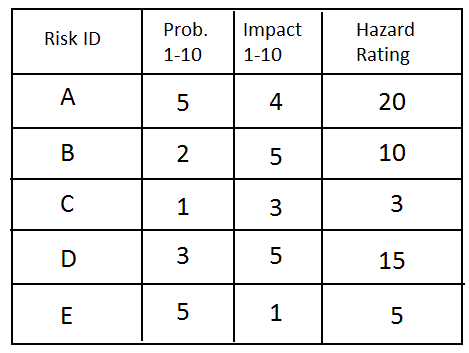
Method Two – Graphical
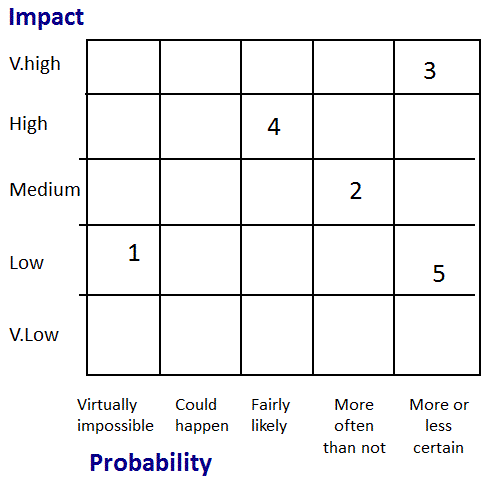
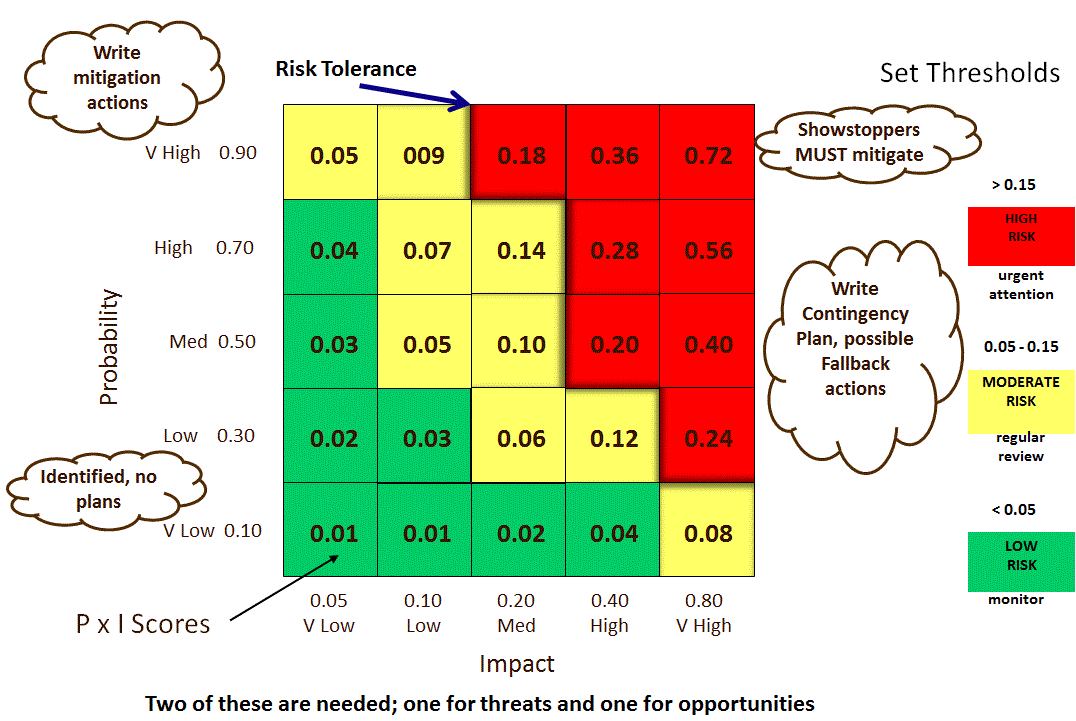
Probability Impact Grid
Risks with low or moderate ratings are:
- taken direct to Plan Risk Responses,
- put onto a Watchlist to watch for changes
- are typically not analyzed quantitatively
Probability Impact (P-I) Matrix
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/uk/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group