Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (United Kingdom)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
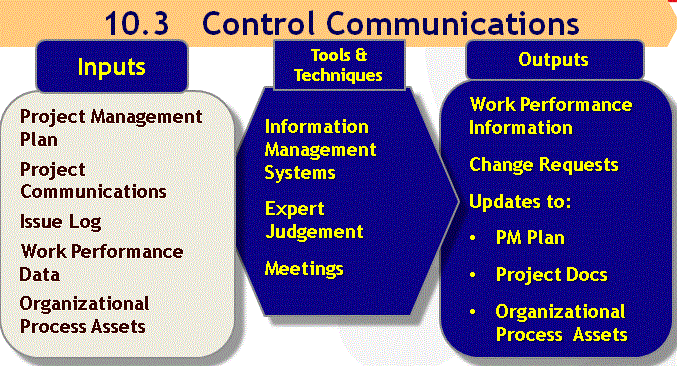
10.3 Control Communications
"The process of monitoring and controlling communications throughout the entire project life cycle to ensure the information needs of the project stakeholders are met."
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc.,
Communications
- Iterative processes
- Right message to the right people at the right time
- Repeating previous information may be better than no message at all
- Monitoring communications and their impacts, feeding through to revisions if required
- Includes status reports, progress measurements and forecasts.
Tools & Techniques
Information Management Systems
- Set of standard tools
- Capture, story and distribute information
- About costs, schedule progress and performance in the project
Reporting systems
- May include tables, reports, spreadsheets, presentations, summarised analyses.
Performance Reports
Report on the
- Results of analysing past performance
- Analysis of actuals against baseline
- Current status of the project – risks and Issues
- Work completed during this reporting period
- Work to be completed during next reporting period
- Summary of changes approved
- Performance of the project
- Forecasts of the project outcome by projecting progress over time.
How to Measure Work Progress
During a team checkpoint meeting:
Ask team members for percentage complete of each work package
- Actuals can be subjective
Or you could apply one of these rules on every work package
- 50/50
- 0/100
- 20/80
- These allow for consistency but do not reflect actuals
Reporting
Can be verbal (high media richness) or written (low media richness)
- a report can not reproduce visual social cues such as gestures and is a low rich communication medium
- video conferencing is able to communicate gestures – high rich
Apply communication theory
- Identify receiver's requirements
- Clearly define objective
- Give only what is needed
- "Flag up" exceptions (RAG system) State problems
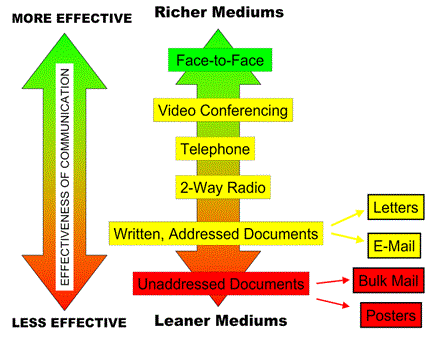
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Media_richness_theory
Creating a Report
Apply a logical structure which should include:
- A beginning – why the report has been written
- A middle, which contains the facts you have assembled and your analysis of those facts
- An end, in which conclusions and recommendations are set out
- A summary of conclusions and recommendations, if the report is lengthy/complex
- An appendices for complex tables and lengthy supporting material
- A contents – only necessary for a long report, but potentially very helpful to the reader.
Use plain words/be succinct
Advantages:
- Likely to be well thought out
- Can present a lot of information
- Provides a record /can reach a large audience.

http://www.fda.gov/downloads/safety/safetyofspecificproducts/ucm180520.pdf
Performance Reporting
- Reactive not proactive
- Contains measurements against the performance management baseline (scope, schedule and cost baselines)
- Report on performance against cost, schedule, scope and quality
- Helps to forecast forward
- Get feedback as well
- Exam viewpoint
The reports should be truthful and not hide what is happening
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/uk/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group