Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (Danmark)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
12.3 Control Procurements
"The process of managing procurement relationships, monitoring contract performance and making changes and corrections to contracts as appropriate."
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
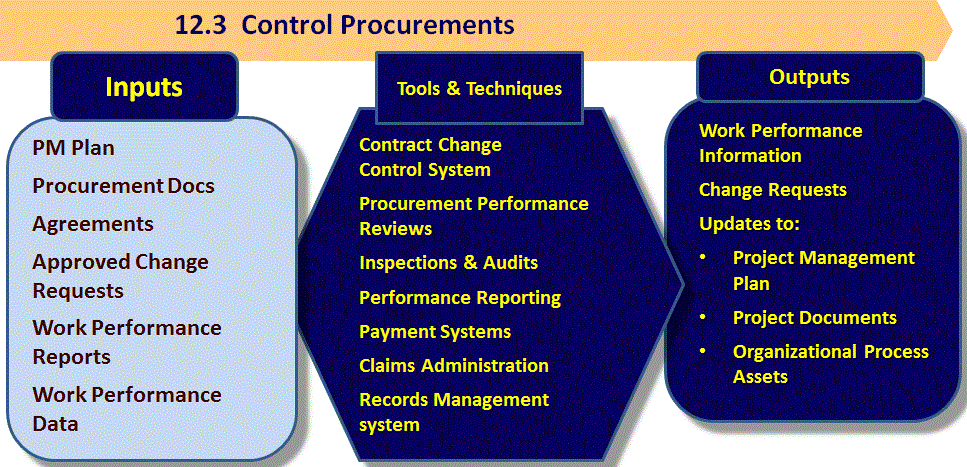
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 12-6 Page 379
Both parties need to ensure each:
- Meet their contractual obligations
- Protect their own legal rights
- Manage own interfaces with subcontracted parties
Administrative changes
- These are the non-substantive and most common changes to the way the contract is administered.
Contract modification
- Substantive changes include a new deadline or changed product requirements.
Supplemental agreement
- An additional agreement related to the contract but negotiated separately.
Constructive changes
- Changes that the seller may have caused through action or inaction.
During the Process
PM – awareness of contractual obligations:
- For self and the PM team to undertake
- For seller PMs and their teams to provide against
- For measurement of work performance -> drive corrective actions as required (4.5 Perform Integrated Change Control)
- Monitor payments made by Procurement against the seller progress/performance ( -> 6.7 Control Schedule and 7.4 Control Costs)
- Record observed seller competency in delivering work for Lessons Learned for future projects
- In case of failure to meet standards, etc… record such to underpin early termination of contract/agreement
Tools and Techniques
Contract Change Control System
- A system to control all changes to procurement contracts, includes all documentation, tracking systems, dispute resolution procedures and approval levels
Procurement Performance Reviews
- Reviews of actual performance of sellers as compared to the contract, in a structured way. Identifies successes and failures (gold plating?)
Inspections and audits
- Conducted by the buyer and supported by the seller Performance reporting on seller performance
Payment Systems & Claims Administration
- Contested changes – negotiation has failed
- Subject to alternative dispute resolution and appeals procedures (next slide)
Records management system
Other Points
Negotiated Settlements
- Dispute resolution – negotiation is win – win for both
- Otherwise mediation,
- Or arbitration
- Or litigation in court
The PMI assumes that:
- Suppliers must be actively managed
- The PM is taking steps proactively to manage suppliers
- All processes and procedures are being followed or implemented, including inspections and audits
- The contract substantively rewards good behaviour and discourages poor performance
OPAs updated include:
- Lessons learned and correspondence with sellers
- Documentation recording evaluated seller performance
- Payment documentation – schedules and payments made
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/dk/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group