Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (Danmark)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
4.5. Perform Integrated Change Control
The process of: "Reviewing all change requests and approving changes and managing changes to:
- Deliverables,
- Organizational Process Assets,
- Project Scope Statement
- Project Management Plan
- Happens throughout the project
- Process is specified in the change control and configuration control systems"
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
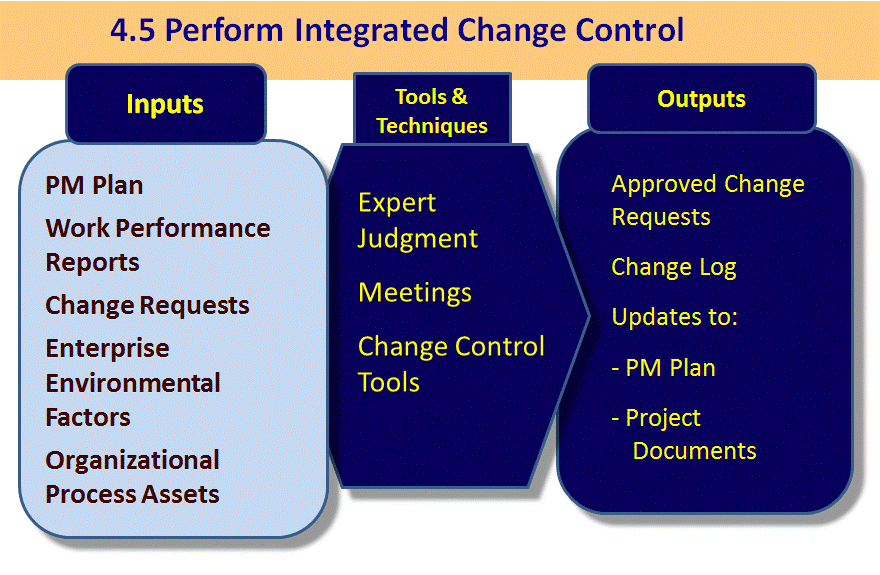
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 4-10 Page 95 Guide)
Change Control System
- A collection of formal documented procedures that define how project deliverables and documentation will be controlled, changed and approved.
- Is a subset of the Configuration Management System
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
- Define
- A value-based process for change-related decision making (CSFs)
- Responsibilities for change decisions
- Review Change Management Plan
- Gain buy-in and commitment of project team
- Get sponsor and key stakeholders agreement.
Change Terms
Change Requests -Requests to expand or reduce the project scope, modify policies, processes, plans, or procedures, modify costs or budgets, or revise schedules
- Oral or written, formal or informal, change requests can include corrective action, preventive action and defect repair.
- PMI stance – should be written
- Approved by the Project Sponsor or the Change Control Board (CCB).
- Project Manager advises on change implications.
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
Change Control Board
- A formally chartered group responsible for reviewing, evaluating, approving, delaying or rejecting changes to the project and communicating these decisions. Power and responsibilities agreed by the stakeholders.
- CCB may be responsible for defining the Change Control process, communication, implementation of the approved CRs.
- A large project may have more than one CCB, with each level having their authority clearly defined to certain levels of change
- The Customer or Sponsor may be part of, or above, the CCB. If above, they may have higher decision making powers
- Needs to be specified decision making authority levels, and maybe, a procedure for an emergency requiring automatic approval
Types of Change
Remember what these mean:
Corrective action - An intentional activity that realigns project work performance with the Project Management Plan
Preventive action - An intentional activity to ensure the future performance of the project work is aligned with the PM Plan
Defect Repair (off specification) - An intentional activity to modify a nonconforming product or its component
The above may lead to updates to the PM Plan
The Change Control Procedure
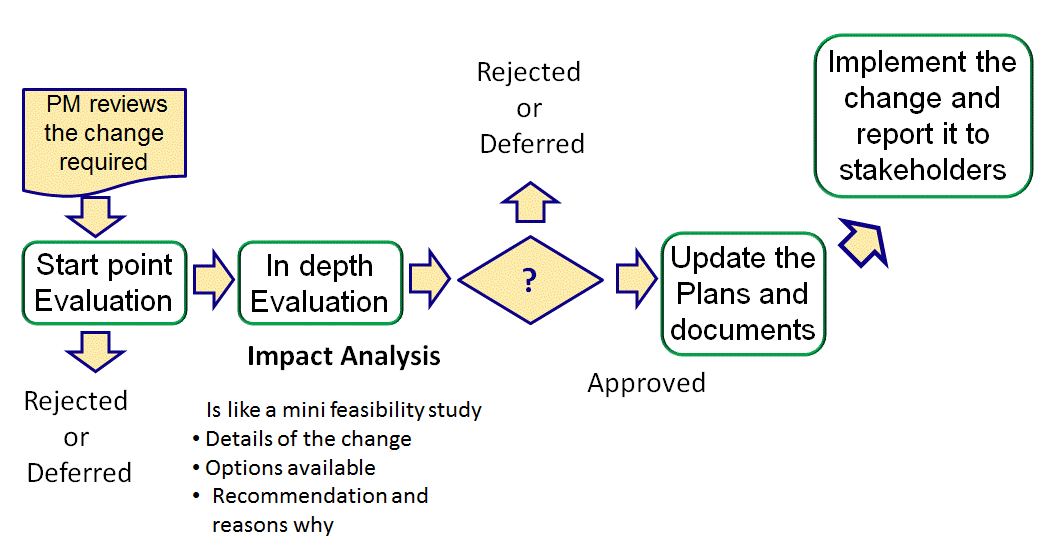
There can be up to 15 questions on this topic in the PMP exam
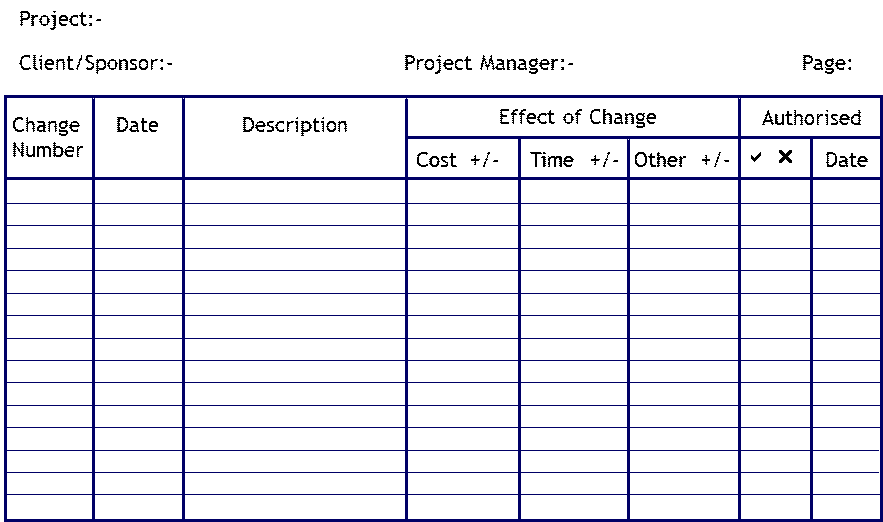
Change Log - Example
Configuration Management
- A subset of the overall project management system
- It is a collection of formal documented procedures used to apply technical and administrative direction and surveillance to:
- Identify and document the functional and physical characteristics of a product, result, service or component
- Control any changes to such characteristics
- Record and report each change and its implementation status
- And support the audit of the products, results or components to verify conformance to requirements
- It includes the documentation, tracking systems and defined approval levels necessary for authorizing and controlling changes
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
Configuration Management
- Ensures the actual product and it's documentation remain consistent.
- Establishes and maintains consistency of a system's or product's performance and its functional and physical attributes, with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life.
- Once a product is baselined, no changes should be made to it without formal change control.
- A Change Freeze may be appropriate towards the project end.
- Further change could risk not meeting the project objectives
Five Functions of Configuration Management
Planning
- Understanding what level of configuration management to apply in the project
- What records will be kept; where the configuration library will be; the structure of the configuration database
Idenitfication
- Being able to identify each project deliverable – Configuration identifier
Control
- Baselining deliverables; release management; protecting against further change without a CCB decision; storing configuration items; keeping the master and giving out copies
Status Accounting
- Identifying the status of deliverables from specification through to baselining, as work is started and completed
Verification/Audits
- An independent check of physical state versus recorded state, to ensure data integrity in performance and progress reporting
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/dk/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group