Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (Danmark)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
9.3 Develop Project Team
"The process of improving competencies, team member interaction and overall team environment to enhance project performance."
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
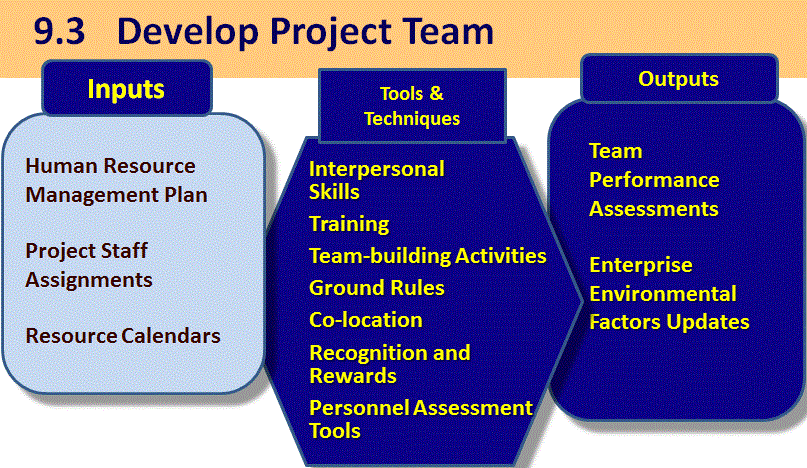
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 9-9 Page 273
Teamwork is a critical factor for project success
Developing effective project teams is a project manager’s primary responsibility
A team is:
- A group of people with different but complimentary skills
- Working to a common purpose, vision and project objectives
- Accountable for their actions, taking the risk of conflict but working to resolve it
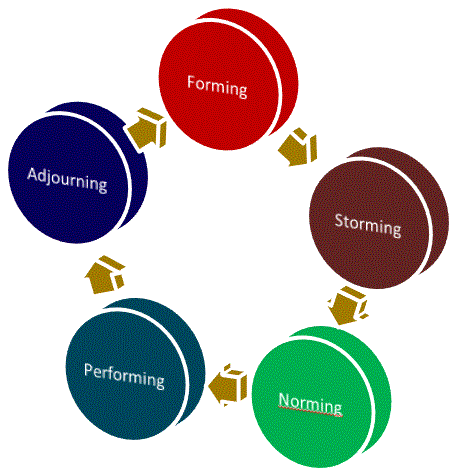
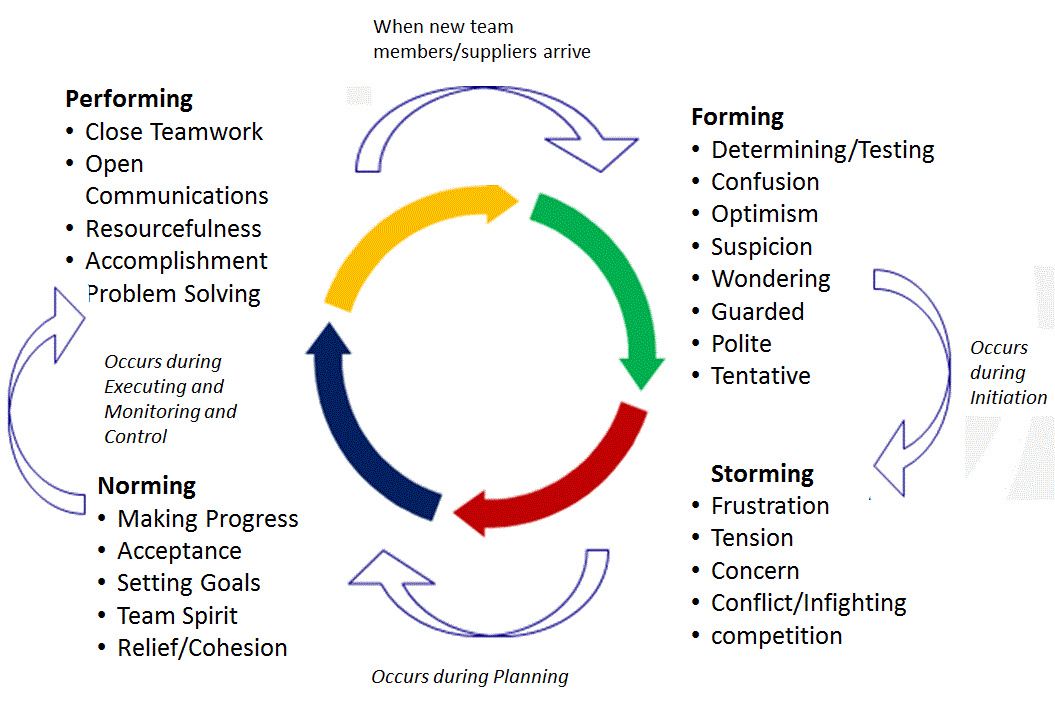
Bruce Tuckman: Ladder of Team Development
Forming
- The team members get to know each other and trust one another.
Storming
- Team members begin to assert themselves and control issues as they emerge. They resolve conflicts and achieve consensus.
Norming
- The team begins to work productively, without worrying about personal acceptance or control issues.
Performing
- The team is working at optimum productivity and are collaborating easily, communicating freely, and solving its own conflict problems.
Adjourning
- The team members complete their assigned work and shifts to the next project or assigned task.
Question
You are 4 months into your project to build and implement a bespoke sales CRM system which is integrated with HR for employee and supplier data.
You have increasingly seen signs of tension within two of your 15 teams and last week, there was a noticeable frosty atmosphere between 4 sets of coders from two separate sellers, after a new supplier was brought in to develop the next phase of functionality
Which phase of team development are you in?
A. Storming as this is just a passing phase and this level of conflict is to be expected
B. Forming as they are just “being lads” and will soon settle down
C. Norming as these differences will resolve themselves very quickly
D. Lazing because you have not attended to their needs yet
Is this better?
Training
Steps taken to acquire or improve knowledge, skills, or attitude(s).
Covers whatever topics are needed
Comes in many forms:
- On the job; off the job
- Reading, online, webinars, seminars
- Single/Multi-day, formal workshops.
- Coaching and mentoring
- Buddy systems
- Team Building Activities
PMBOK says training
- Could be charged to the project budget
- Or borne by the seller if useful on future projects
Role of a PM or Junior PM
- Provide a vision
- Agree goals and targets
- Agree plans and allocate tasks
- Provide support and resource
- Give and receive information
- Exercise many skills:
- Summarizing
- Clarifying
- Motivating
- Counseling
- Communicating
- Coaching
- Monitoring
- Create a climate of openness and trust.
Team-building activities
Designed to help team members work together more effectively and develop better working relationships:
- Experiential off-site workshops e.g. Building a raft, a tower from A4 sheets of paper, a maze
- Communications training
- Conflict resolution
- Planned team outings
- Shared space, publicity and symbols to create a team identity
Interpersonal skills: PMBOK Appendix X3
Interpersonal Skills Include:
Communication
- verbal – 7%
- non verbal – 55%
- paralinguistic – 38% (the way the words are said)
(http://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/beyond-words/201109/is-nonverbal-communication-numbers-game)
Emotional Intelligence
- “Know your staff”
- Understand and acknowledge concerns
- Resolve people issues quickly
Assertiveness and Confidence Building
- May need to do this as part of using emotional intelligence intelligently
Negotiation and Conflict Resolution
- Later in Communications Management
Influencing Skills and Building Trust
Team Building and Facilitation
Stakeholder Engagement
Interpersonal skills for a Project Manager
Managers do things right while Leaders do the right thing
Leadership – ability to make things happen
- Communicate the vision
- Strong and inspirational
- Vary style according to the needs of the situation
- Directive/assertive
- Delegative – involves letting go to a degree
- Facilitational – empowering whilst stepping back
- Supportive – showing trust in them to go and do
- Flexible according to the needs of the situation (Hersey and Blanchard “Situational Leadership)
Influencing
- Collect information; Talk and listen
- Understand
- Give/Develop understanding
- Persuade others to ones own point of view/seeing weakness in theirs
Decision making
- Focus on goals and targets
- Stimulate team creativity
- Negotiate and influence
- Manage opportunity and risk
Build Trust
Reward and Recognition Systems
- Reinforcing performance or behavior systematically
- Motivating the team to perform better
- Rewards include:
- Additional vacation time or other perks.
- Awards or trophies; Gifts; a bonus
- Training or role rotation opportunities
- Recognition and Praise
Ground Rules:
- Allows team members to discover values that are important to one another as well as to share their commitment to the rules
- Can be Implicit or explicit
- Establishes expectations as to what is acceptable / unacceptable behaviors
Personnel Assessment Tools
- Attitudinal Surveys
- Competency Assessment Centres
- Structured test (in tray exercise)
- Aptitude (Numerical, verbal and logical reasoning tests)
- Structured Interviews
- Interview Assessment Plan
- Ability Tests
- Aptitude Tests (SHL; 16pf; OPQ; Thomas International)
- Focus Groups
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
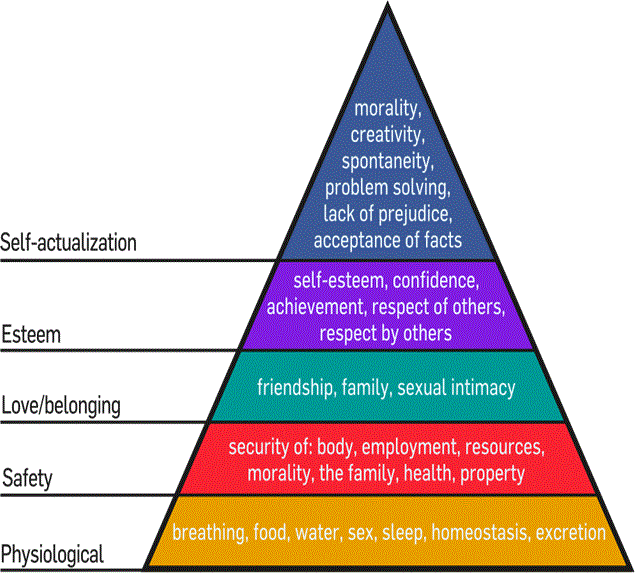
Source http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maslow%27s_hierarchy_of_needs
- An individual moves through these levels during their lifetime
- Goes up and can come down
- Redundancy
- Career change
- Mid life crisis
- Helps us to manage by understanding our team and where they are in this model.
- Model subsequently updated later to include a top layer of Self Transcendence
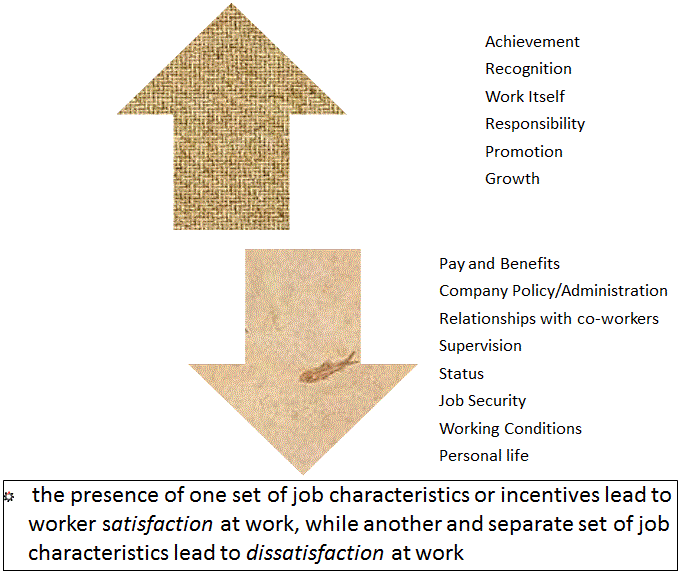
Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene Theory
Motivators
- Achievement
- Recognition
- Work Itself
- Responsibility
- Promotion
- Growth
Hygiene Factors
- Pay and Benefits
- Company Policy & Administration
- Relationships with co-workers
- Supervision
- Status
- Job Security
- Working Conditions
- Personal life
McGregor
Theory X
The average worker is
- Inherently lazy
- Must be supervised
- Threat of punishment needed
- Does not like responsibility
Theory Y
The average worker is
- Not resistant to organizational change
- Eager for responsibility
- Self motivated, does not require constant supervision
- Wants personal improvement and self respect
Source: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yR03d9gN1nw
Ouchi Theory Z
Best of Theory Y with:
Strands of modern Japanese management thinking
- Freedom
- Trust
- Loyalty
- Interest
More reliance on attitude and responsibilities of the workers
David McClelland – Theory of Needs
- Human Behaviour is affected by three needs – for:
- Power – the ability to influence others to achieve your own wishes
- Achievement – urge to excel, strive to succeed
- Affiliation – open and meaningful relationships with others, based on cooperation and understanding
- People with high achievement needs are highly motivated by competing and challenging work
- Those motivated by power have a strong urge to be influential and controlling
- Others motivated by affiliation want to be in a friendly and supportive environment, want to be in “good books” – cannot be good leaders.
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/dk/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group