Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (Danmark)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
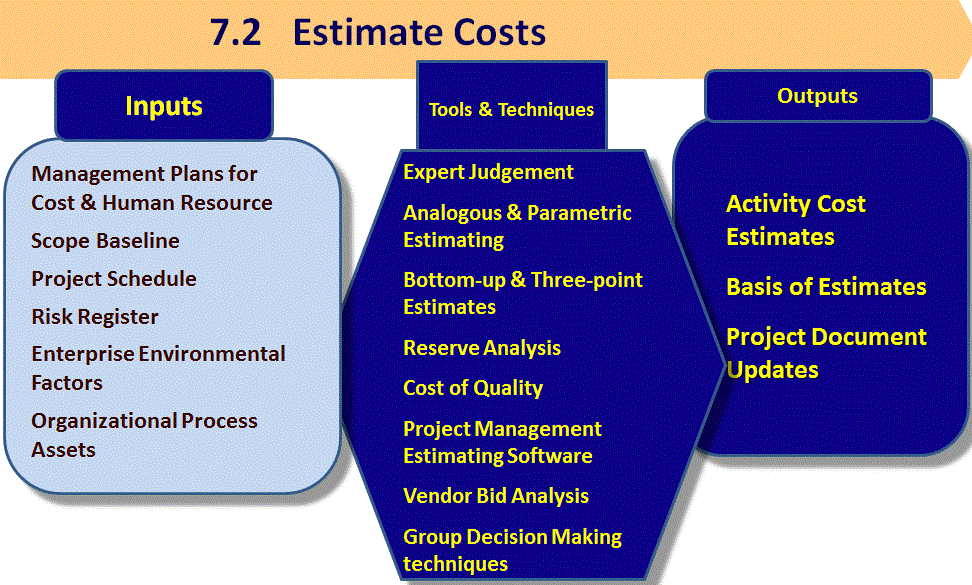
7.2 Estimate Costs
"The process of developing an approximation of the monetary resources needed to complete project activities."
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 7-4 Page 200
- The process of developing an understanding of what resources are needed for the project activities identified.
- Usually expressed in monetary terms, other units such as person hours or staff days can often be used.
- Project resources include labor, materials, equipment, meeting rooms, facility fees and services
Tools and Techniques
Analogous Estimating
- Uses historical information, expert judgment.
- Think “analogy” – something similar
- Relatively quick and low cost to produce
Used when:
- Only limited information available.
- Similar project information available
- Estimators have right experience.
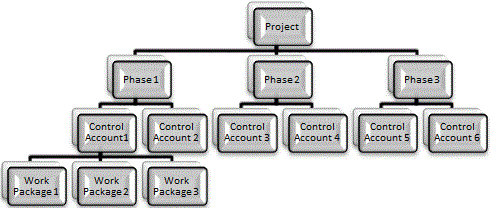
Bottom Up Estimating
- Estimates the cost for each work package.
- Estimates are then rolled up (aggregated).
- Same technique as used for resource estimating
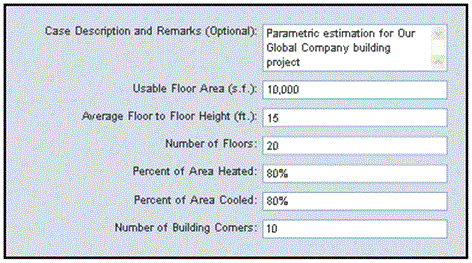
Parametric Estimating
- Used to predict total project costs by using project's characteristics in a mathematical model.
- Cost/m2, number of bricks/wall, plumbers/2 storey building.
- Degree of accuracy depends on the integrity of the information used
Other Tools and Techniques in your Toolkit
Three Point Estimating
- Triangular Distribution = (O + M + P) / 3
- Beta Distribution = (O + 4M + P) / 6
Reserve Analysis:
- A cost contingency reserve may be used to account for cost associated risks
Cost of Quality (COQ) PM
Estimating Software
- Simplify cost estimations and allow for rapid review of estimate alternatives
Vendor Bid Analysis
- Responses from bidders will indicate what a project or deliverables should cost
Group Decision Making Techniques
'Soft' Estimating – Analogous Approach
Examples breakdown of a project's stage effort (in a software project):
Stage |
% of Total |
Preliminary Survey |
1 |
Feasibility Study |
6 |
Systems Analysis |
14 |
System Design |
16 |
Programming |
27 |
Systems Testing |
13 |
Acceptance Testing |
11 |
Implementation |
12 |
Uncertainty in Cost Estimates
Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimate
- Usually made during Initiation
- -25% to +75%
Budget Estimate
- Usually made during the Planning
- -10% to +25%
Definitive Estimate
- Identified when rolling up the WBS
- -5% to +10%
Need to engage team members using group decision making techniques to improve accuracy of estimates
How to Estimate Project Costs
Some simple steps to take:
- Involve work package owners
- Gather relevant information
- Determine which technique to use.
- Identify alternative costing options.
- Determine which measurement units will be used
- Consider possible risks impacting on costs
- Assign all cost estimates to their account
- Add project overheads – 5% for meetings; 15% for management time; contingency (10 – 12%)
- Adding in company overheads (margin for profit, etc…) will be done later
Basis of Estimates
Providing clear details on how we arrived at the costs estimated:
- How we developed it – the method used
- Assumptions made
- Constraints applied and why
- Range of estimates used and the degree of confidence in using them
- Degree of confidence in the final estimate
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/dk/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group